| Member | Action | Date | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Posted This Week | Learn Blue | Farming Resilience: Unlocking the Artemia Opportunity on Calendar
Join on Webex Artemia (brine shrimp) is a critical live feed in aquaculture, particularly in hatcheries for shrimp, fish, and ornamental species. Its production and sustainable management are increasingly important as aquaculture expands globally. Artemia also thrives in salt pans and hypersaline ecosystems, presenting unique opportunities for integrated production systems, salt quality enhancement, and ecosystem services. Despite its significance, Artemia resources are often under-managed, subject to unsustainable harvesting, and vulnerable to habitat degradation. At the same time, global Artemia markets face increasing demand, while new innovations in farming, processing, and conservation offer opportunities for inclusive investment, resilience, and biodiversity protection. This event will bring together global experts, policymakers, private sector representatives, and development partners to discuss the state of Artemia production and conservation, market opportunities, regulatory frameworks, and pathways for sustainable and viable investment. |
33 days ago |
||||
|
|
Updated Mapping Côte d’Ivoire Aquaculture Suitability Zones on Documents
The Côte d’Ivoire government views aquaculture as an important instrument for economic growth, poverty reduction, and food and nutrition security. As part of a wider array of actions to boost the sector and achieve the goals set in the Côte d’Ivoire Strategic Aquaculture Transformation Programme , the government partnered with the World Bank’s AquaInvest Platform , funded by PROBLUE (a multi-donor trust fund administered by the World Bank) to support aquaculture suitability mapping and planning. Sustainable and resilient aquaculture development is founded on comprehensive and reliable spatial information which is essential for identifying the best locations for aquaculture businesses, assessing risks, conducting due diligence on proposed aquaculture investments, and facilitating licensing and monitoring. More: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/b0f0f37f8ff9405d83b082e84d1d6416 |
Jul 21 2025, 4:00 PM |
||||
|
|
Posted Mapping Côte d’Ivoire Aquaculture Suitability Zones on Documents
The Côte d’Ivoire government views aquaculture as an important instrument for economic growth, poverty reduction, and food and nutrition security. As part of a wider array of actions to boost the sector and achieve the goals set in the Côte d’Ivoire Strategic Aquaculture Transformation Programme , the government partnered with the World Bank’s AquaInvest Platform , funded by PROBLUE (a multi-donor trust fund administered by the World Bank) to support aquaculture suitability mapping and planning. Sustainable and resilient aquaculture development is founded on comprehensive and reliable spatial information which is essential for identifying the best locations for aquaculture businesses, assessing risks, conducting due diligence on proposed aquaculture investments, and facilitating licensing and monitoring. More: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/b0f0f37f8ff9405d83b082e84d1d6416 |
Jul 21 2025, 4:00 PM |
||||
|
|
Updated Mapping Côte d’Ivoire Aquaculture Suitability Zones on Documents
The Côte d’Ivoire government views aquaculture as an important instrument for economic growth, poverty reduction, and food and nutrition security. As part of a wider array of actions to boost the sector and achieve the goals set in the Côte d’Ivoire Strategic Aquaculture Transformation Programme , the government partnered with the World Bank’s AquaInvest Platform , funded by PROBLUE (a multi-donor trust fund administered by the World Bank) to support aquaculture suitability mapping and planning. Sustainable and resilient aquaculture development is founded on comprehensive and reliable spatial information which is essential for identifying the best locations for aquaculture businesses, assessing risks, conducting due diligence on proposed aquaculture investments, and facilitating licensing and monitoring. More: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/b0f0f37f8ff9405d83b082e84d1d6416 |
Jul 21 2025, 4:00 PM |
||||
|
|
Posted Promoting Integrated and Restorative Aquaculture in World Bank Investment Operations on Calendar
WebEx Link: Join on Webex As the demand for sustainable aquaculture intensifies, due to climate pressures, biodiversity loss, and food system transformation, there is an urgent need to embed ecosystem-based, resource-efficient, and nature-positive aquaculture models into country programs. This event is part of Learn Blue, a training program which offers World Bank Group staff and external experts the opportunity to learn about blue economy tools and activities. This event is organized by the Integrating Aquaculture into Land and Seascape Programs ASA and designed to build capacity of teams involved in design and implementation of aquaculture projects. The ASA is supported by PROBLUE and PROGREEN, trust funds administered by the World Bank. For any questions about the webinar please contact Dijana Ferizovic.
|
Jun 11 2025, 9:28 AM |
||||
|
|
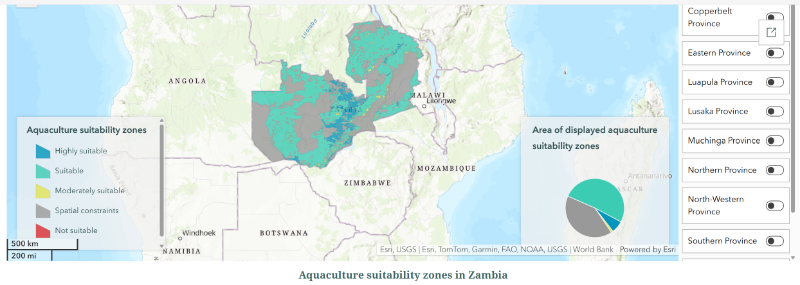
Posted Mapping aquaculture suitability in Zambia on Documents
The Government of Zambia has partnered with the World Bank, including the AquaInvest Platform , funded by PROBLUE , a multidonor trust fund administered by the World Bank, to carry out strategic assessment of aquaculture development priorities. Mapping aquaculture suitability of Zambia enables determination of the country’s full potential and opens possibility to plan for sector growth. Aquaculture spatial planning serves as a critical building block in Zambia's overall strategic objectives to alleviate poverty, create livelihoods and jobs around aquaculture, conserve biodiversity and reduce climate change impacts. While developing the aquaculture regulatory framework, special attention to the instruments of resolving conflicts between competing usage of finite natural resources is critical. Spatial planning is the key among such instruments. Thus, to guide new investments in the aquaculture sector, the assessment identified aquaculture suitability zones in the country, using the Multi-Criteria Evaluation, a well-tested methodology for aquaculture site selection and spatial planning studies. It specifies, creates, and aggregates comprehensive sets of evaluation criteria which inform the decision-making process (see specific criteria applied to situation in Zambia below). The resulting zoning is available in format allowing the development of public-facing applications, such as the Map of Potential Aquaculture Areas launched by Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock , and integration with initiatives like the 2023 National Fisheries and Aquaculture Policy (NFAP) . The information helps for policy makers, public officials, and private sector representatives to save time and resources while identifying optimal sites for new aquaculture enterprises. Zambia Aquaculture Sector With high levels of poverty ( 64.3% of population living on less than US$2.15 a day in 2022 ), rural poverty, and food insecurity ( 32.1% of total population in 2022 ) Zambia depends on the economic opportunities provided by its natural resources. The country’s water bodies and wetlands, covering 1.6% and 19% of its territory, provide it with reliable resources for fisheries and aquaculture. According to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), fisheries and aquaculture contribute approximately 2% of Zambia's GDP, with fish accounting for 30% of the national dietary animal protein . Fish and seafood consumption in Zambia remains at approximately 13 kg per person annually (2017-2019), below the global average of 20.4 kg . Increasing aquaculture production could help address food insecurity, which particularly affects children. In 2022, among Zambian children under 5 years old, the prevalence of wasting was at 4.2% and of stunting at 31.4% . According to FAO , total aquaculture and fisheries production in Zambia reached 185,076 tons in 2022, with aquaculture contributing 41%—a significant increase from 13% a decade ago. Fast growth in aquaculture has driven the 84% increase in aquatic products output in Zambia since 2012. Please visit: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/be47e93d7bc04de8bf59eb4451967fba
|
Apr 21 2025, 4:01 PM |
||||
|
|
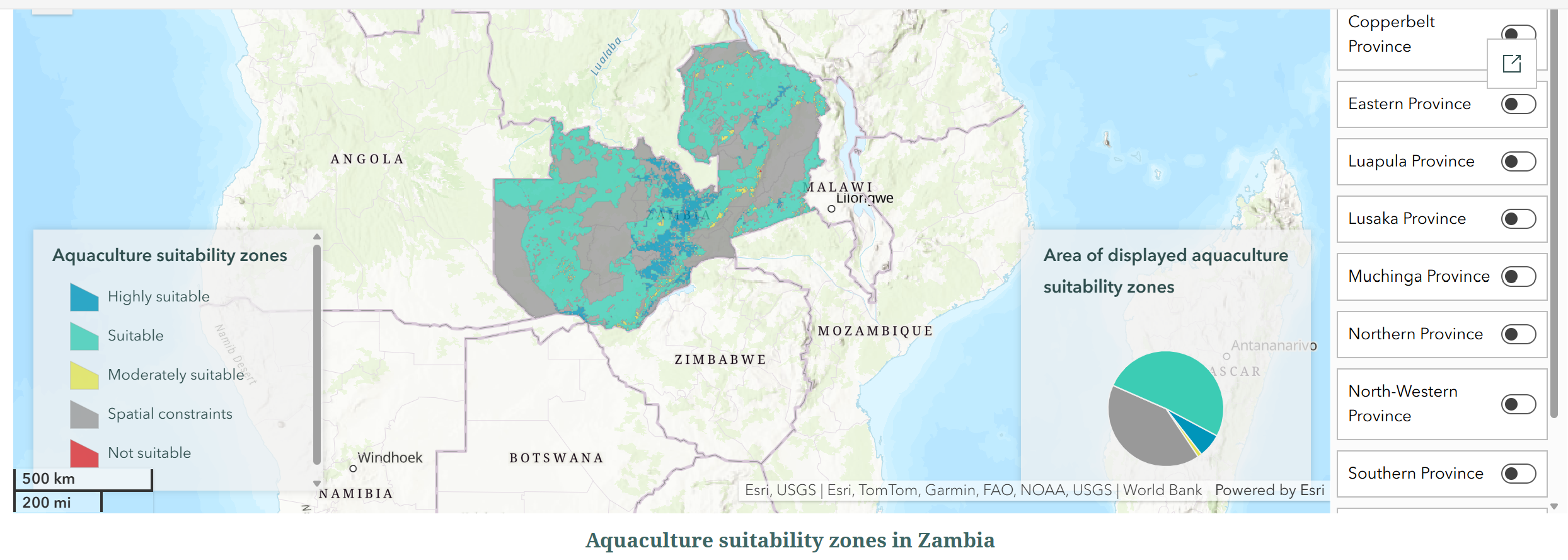
Updated Mapping aquaculture suitability in Zambia on Documents
The Government of Zambia has partnered with the World Bank, including the AquaInvest Platform , funded by PROBLUE , a multidonor trust fund administered by the World Bank, to carry out strategic assessment of aquaculture development priorities. Mapping aquaculture suitability of Zambia enables determination of the country’s full potential and opens possibility to plan for sector growth. Aquaculture spatial planning serves as a critical building block in Zambia's overall strategic objectives to alleviate poverty, create livelihoods and jobs around aquaculture, conserve biodiversity and reduce climate change impacts. While developing the aquaculture regulatory framework, special attention to the instruments of resolving conflicts between competing usage of finite natural resources is critical. Spatial planning is the key among such instruments. Thus, to guide new investments in the aquaculture sector, the assessment identified aquaculture suitability zones in the country, using the Multi-Criteria Evaluation, a well-tested methodology for aquaculture site selection and spatial planning studies. It specifies, creates, and aggregates comprehensive sets of evaluation criteria which inform the decision-making process (see specific criteria applied to situation in Zambia below). The resulting zoning is available in format allowing the development of public-facing applications, such as the Map of Potential Aquaculture Areas launched by Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock , and integration with initiatives like the 2023 National Fisheries and Aquaculture Policy (NFAP) . The information helps for policy makers, public officials, and private sector representatives to save time and resources while identifying optimal sites for new aquaculture enterprises. Zambia Aquaculture Sector With high levels of poverty ( 64.3% of population living on less than US$2.15 a day in 2022 ), rural poverty, and food insecurity ( 32.1% of total population in 2022 ) Zambia depends on the economic opportunities provided by its natural resources. The country’s water bodies and wetlands, covering 1.6% and 19% of its territory, provide it with reliable resources for fisheries and aquaculture. According to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), fisheries and aquaculture contribute approximately 2% of Zambia's GDP, with fish accounting for 30% of the national dietary animal protein . Fish and seafood consumption in Zambia remains at approximately 13 kg per person annually (2017-2019), below the global average of 20.4 kg . Increasing aquaculture production could help address food insecurity, which particularly affects children. In 2022, among Zambian children under 5 years old, the prevalence of wasting was at 4.2% and of stunting at 31.4% . According to FAO , total aquaculture and fisheries production in Zambia reached 185,076 tons in 2022, with aquaculture contributing 41%—a significant increase from 13% a decade ago. Fast growth in aquaculture has driven the 84% increase in aquatic products output in Zambia since 2012. Please visit: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/be47e93d7bc04de8bf59eb4451967fba
|
Apr 21 2025, 4:01 PM |
||||
|
|
Updated Mapping aquaculture suitability in Zambia on Documents
The Government of Zambia has partnered with the World Bank, including the AquaInvest Platform , funded by PROBLUE , a multidonor trust fund administered by the World Bank, to carry out strategic assessment of aquaculture development priorities. Mapping aquaculture suitability of Zambia enables determination of the country’s full potential and opens possibility to plan for sector growth. Aquaculture spatial planning serves as a critical building block in Zambia's overall strategic objectives to alleviate poverty, create livelihoods and jobs around aquaculture, conserve biodiversity and reduce climate change impacts. While developing the aquaculture regulatory framework, special attention to the instruments of resolving conflicts between competing usage of finite natural resources is critical. Spatial planning is the key among such instruments. Thus, to guide new investments in the aquaculture sector, the assessment identified aquaculture suitability zones in the country, using the Multi-Criteria Evaluation, a well-tested methodology for aquaculture site selection and spatial planning studies. It specifies, creates, and aggregates comprehensive sets of evaluation criteria which inform the decision-making process (see specific criteria applied to situation in Zambia below). The resulting zoning is available in format allowing the development of public-facing applications, such as the Map of Potential Aquaculture Areas launched by Ministry of Fisheries and Livestock , and integration with initiatives like the 2023 National Fisheries and Aquaculture Policy (NFAP) . The information helps for policy makers, public officials, and private sector representatives to save time and resources while identifying optimal sites for new aquaculture enterprises. Zambia Aquaculture Sector With high levels of poverty ( 64.3% of population living on less than US$2.15 a day in 2022 ), rural poverty, and food insecurity ( 32.1% of total population in 2022 ) Zambia depends on the economic opportunities provided by its natural resources. The country’s water bodies and wetlands, covering 1.6% and 19% of its territory, provide it with reliable resources for fisheries and aquaculture. According to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), fisheries and aquaculture contribute approximately 2% of Zambia's GDP, with fish accounting for 30% of the national dietary animal protein . Fish and seafood consumption in Zambia remains at approximately 13 kg per person annually (2017-2019), below the global average of 20.4 kg . Increasing aquaculture production could help address food insecurity, which particularly affects children. In 2022, among Zambian children under 5 years old, the prevalence of wasting was at 4.2% and of stunting at 31.4% . According to FAO , total aquaculture and fisheries production in Zambia reached 185,076 tons in 2022, with aquaculture contributing 41%—a significant increase from 13% a decade ago. Fast growth in aquaculture has driven the 84% increase in aquatic products output in Zambia since 2012. To learn more about the Mapping aquaculture suitability in Zambia Please visit: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/be47e93d7bc04de8bf59eb4451967fba
|
Apr 21 2025, 4:01 PM |
||||
|
|
Posted Artemia: Small Shrimp – Big Business – Climate-smart Superfood on Calendar
This webinar will focus on artemia, a small brine shrimp found naturally in hypersaline ecosystems – salt lakes, salt pans and salt works across the world. Presenters will explain artemia’s unique role in the aquatic ecosystem and explore ways for future investment opportunities.
|
Mar 07 2025, 8:39 AM |
||||
|
|
Posted Learn Blue | Improving Animal Welfare in Aquaculture on Calendar
With the rising global demand for protein, aquaculture has become the dominant provider of sustainable seafood. Just as in terrestrial farming, sustainable aquaculture depends on maintaining the health and welfare of aquatic animals. Animal welfare in aquaculture is important for ethical, environmental, and economic reasons.
|
Feb 11 2025, 11:28 AM |