Transforming Agriculture and Food Systems through Data-driven Digital Agriculture: Learning from Practitioners
Please Enroll: https://olc.worldbank.org/content/transforming-agriculture-and-food-systems-through-data-driven-digital-agriculture-learning-0
Highlights: Cultivhacktion – Indonesia Digital Agriculture Hackathon
Watch the recorded video of Cultivhacktion – Indonesia Digital Agriculture Hackathon
Read the Blog Investing in data and innovation ecosystem to transform Indonesia’s agriculture
Watch the recorded webinar on CultivHacktion- Data Hackathon: Harvesting Innovations for Agricultural Transformation in Indonesia (English)
Watch the recorded webinar on CultivHacktion- Data Hackathon: Harvesting Innovations for Agricultural Transformation in Indonesia (Indonesian Bahasa)
Just released report on Digital Revitalization of the Agri-food Sector in Mashreq Focus on Iraq, Jordan, and Lebanon. The Mashreq countries of focus (Iraq, Jordan, and Lebanon) have significant comparative advantage for exporting high-value fresh products to premium markets and expanding water-efficient agricultural production. Stimulating the agriculture sector will also stimulate other economic sectors in all three countries, supporting input supplies, food processing, logistics, and financial services. Supporting agriculture provides an economy-wide multiplier effect.
Digital Agriculture Profiles Turkey, Kenya, Argentina, Vietnam, South Africa, Rwanda, and Côte d'Ivoire
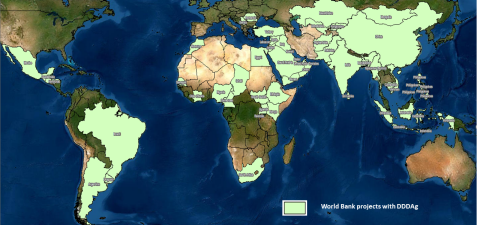
Digital technologies are slowly spreading in agriculture sectors globally. But their adoption is hampered by the digital divide which requires significant public investments, improved policy and incentive frameworks to be bridged. Only after that, digital transformation will take place at scale. Digital Agriculture Profile (DAP) is meant to assess the country's readiness for this digital transformation by identifying main bottlenecks, opportunities and risks for digital transformation. DAP will thus guide public investment and policy work to accelerate the scaling up of digital transformation. Please click the respective links to download DAP of Turkey, Kenya, Argentina, Vietnam, South Africa, Rwanda, and Côte d'Ivoire
Digital Agriculture: New Frontiers for the Food System March 17th, 2021
Rising food insecurity and malnutrition, combined with high food loss and waste, agricultural pollution and persistent poverty, show that the world’s food system is not fit for purpose—and COVID-19 has only worsened existing fault lines in the food and agriculture sector. The ongoing digital revolution could be transformative for food and agriculture, and create more efficient, equitable, and environmentally sustainable ways to feed the world. Click the image or link above to watch the recorded video.
The new book “What’s cooking: the digital transformation of the agrifood system” which proposes a roadmap through which data and digital technologies can lead to efficient, equitable and environmentally sustainable food systems, and looks at the role of the public sector in ensuring these outcomes are maximized.
Citation “Schroeder, Kateryna; Lampietti, Julian; Elabed, Ghada. 2021. What's Cooking : Digital Transformation of the Agrifood System. Agriculture and Food Series;. Washington, DC: World Bank. © World Bank. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/35216 License: CC BY 3.0 IGO.” URI http://hdl.handle.net/10986/35216
Beyond the Pandemic: Harnessing the Digital Revolution to Set Food Systems on a Better Course by Julian Lampietti, Ghada El Abed, and Kateryna Schroeder
One of the most striking images of the coronavirus pandemic is the contrast between farmers dumping milk, smashing eggs, and plowing vegetables back into the soil and consumers facing empty store shelves and long lines at food distribution centers. How is it possible to have over-abundance on one hand and scarcity on the other?
FUTURE of FOOD Harnessing Digital Technologies to Improve Food System Outcomes
This report looks at the opportunities from digital technologies, including better transparency of agricultural value chains, smarter farms, and improved public services. It also reviews some of the risks, including an over-concentration of service provider market power, poor data governance, and exclusion. It presents a set of potential entry points for public sector action to seize the opportunities that expanding rural network coverage can bring while fostering digital entrepreneurship and facilitating demand. Read more
Scaling Up Disruptive Agricultural Technologies in Africa
This study—which includes a pilot intervention in Kenya—aims to further the state of knowledge about the emerging trend of disruptive agricultural technologies (DATs) in Africa, with a focus on supply-side dynamics. The first part of the study is a stocktaking analysis to assess the number, scope, trend, and characteristics of scalable disruptive technology innovators in agriculture in Africa. From a database of 434 existing DAT operations, the analysis identified 194 as scalable. The second part of the study is a comparative case study of Africa’s two most successful DAT ecosystems in Kenya and Nigeria, which together account for half of Sub-Saharan Africa’s active DATs. Scaling Up Disruptive Agricultural Technologies in Africa concludes by establishing that DATs are demonstrating early indications of a positive impact in addressing food system constraints. Read more
HANDBOOK: Digital Financial Services for Agriculture
This handbook offers financial services providers an understanding of smallholder farmers and agricultural value chains, and practical guidance on how to develop and launch sustainable financial services for the agricultural sector. It surveys the current landscape in terms of existing DFS offerings in the agricultural sector, to share actual market experience and lessons learned from the pioneers in the market. Read more
Digital Agriculture Platform Blueprints: A report by Mercy Corps AgriFin, GIZ, and Dalberg
The challenges in agriculture in Africa, particularly for the smallholder farmers producing 80% of its food for consumption, are complex, and no single solution exists to reverse age-old issues around markets, infrastructure, poverty and exclusion. These trends are now further compounded by increased competition over natural resources, massive urban migration and increasing climate-related shocks. Despite these trends, the effective application of digital technology has emerged as a catalytic tool in addressing market gaps and challenges faced in agriculture, including for smallholder farmers at the end of the last mile.
Read moreDigital Technologies in Agriculture and Rural Areas: A report by FAO
The rise of digital agriculture could be the most transformative and disruptive of all the industries, because digital agriculture not only will change how farmers farm their farms, but also will transform fundamentally every part of the agrifood value chain. Digital agriculture will affect the behavior of farmers, and affect the way that input providers, processing and retail companies’ market, price and sell their products. Read more
Digital and Data-Driven Agriculture: Harnessing the Power of Data for Smallholders
Do you know that data-driven agriculture can boost farmers’ productivity? The data has numerous uses in farming, namely planning, monitoring and assessment, event intervention and management, tracing and tracking, market access and negotiations, optimization, and forecasting. In particular, the use of data in agriculture is the future of farming. Reading this article can be an eye-opener for how data could be used to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of agricultural activities. Read more
The Digitalisation Of African Agriculture Report by CTA
Why are digital solutions and agriculture data potentially so transformative? For farmers, they offer access to tailored information and insights that allow individuals to optimize their production, gain access to appropriate products and services, and explore new linkages with markets. D4Ag provides enterprises deeper understanding of their target segments, allowing them to better tailor their interventions to the needs of smallholder farmers. Governments, likewise, can use improved understanding of farmer segments to improve macro-decision policymaking, as well as the design and implementation of their programmes. A report by The Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Cooperation ACP-EU (CTA) Read more
Byte by Byte: Policy Innovation for Transforming Africa’s Food System with Digital Technologies
Did you know that to this day many African farmers do not have access to the market and finances required to maximize their farming profitability and outputs? This article can be useful in providing appropriate and dependable solutions that make use of digital technologies. Specifically speaking, digitizing agriculture leads to proper decision-making, such as knowing when to plant or harvest, and can lead to a sustainable increase of the farming produce. Thus, with digitization, food security in Africa is possible. Read more
















Mail sent to Community Managers, Please access the group once it get approved by Moderator.